14 Cartoons About Machine Espresso To Brighten Your Day
페이지 정보
Author Mitchel 작성일24-05-25 15:00 Views25관련링크
본문
How Does Machine Espresso Work?
Machine espresso utilizes precise pressure and amazing filter technology to make the coffee we love. What exactly does it work?
Espresso is created by forcing hot water under pressure through finely ground coffee. The process is similar to making drip coffee, but the difference is in the pressure.
The Group Head
As the name suggests, the group head is where you insert your portafilter when brewing espresso. It distributes water into the portafilter and regulates the pressure of extraction. There are many different types of group heads, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some are designed to provide temperature stability while others are built to handle pre-infusion. Others are made to control the lever. Some have a combination, such as the E61. This is a preferred choice for baristas because it offers multiple benefits in one package.
As you can see in the image above the group head comes with several notches where you place your portafilter before twisting it manually to secure it. A gasket made of rubber is positioned within the notches to make a seal when you insert your portafilter. The notches allow for the precise placement of the portafilter. This is crucial for an even extraction.
The group head is not just able to allow you to put in your portafilter easily, but it also maintains the temperature at a constant level. It does this by cycling hot water through the brew container and around the portafilter, making sure that it's always at the right temperature to extract. This is vital, because even a small difference in temperature can make the difference between a excellent and great espresso.
The Pump
Unlike manual piston machines, which rely on a lever that pressurize water, rotating espresso machines rely upon motorized pumps that provide the nine atmospheric bars of pressure required to extract espresso. This pressure is built up by pumping water through a heat-exchanger and then through the ground coffee.
Pumps are generally cheaper and last longer than piston-driven machines. However, both kinds of machines may degrade due to excessive use and inadequate cleaning. They also add mechanical complexity which can result in the cost of even the simplest models.
Certain espresso machines utilize steam pressure instead of a pump to brew espresso. This can result in over-extraction because the boiler that makes steam also warms the water to boil. The machines also need to constantly rebuild their pressure between cups. This requires energy and time.
Many espresso machines employ the rotary or vibration pump, which has a vibration model using a vibrating disc to generate the pressure and the rotary model pushing hot water through the grounds under high speed. Both types of machine are capable of producing excellent espresso, but the rotary pumps are quieter, and more durable than vibration pumps.
The Boiler
The boiler is the element that heats water to the optimal temperature to extract. The steam produced reaches the portafilter, which contains the espresso coffee grounds. It is then poured into the cup. In this process, the steam creates pressure to push through the grounds of the coffee. This creates a foam on top of the espresso. This is the hallmark of a great espresso.
There are three kinds of espresso machines, each having a different type of pump and the temperature of the brew. There are different ways to control the amount of brew, as well as the size of cup that can be produced by the machine.
The first espresso machines were steam-types. The earliest espresso machines were steam-type machines. This led to the coffee tasting bitter and Coffeee burnt. This is why Milanese manufacturers Luigi Bezzerra and Desiderio Pavoni invented the modern Gaggia RI8425/11 Espresso Machine: Quality Freestanding Silver machine.
The most well-known espresso maker is a semi-automatic device that has an electric pump. These are the images people have when they think of an espresso maker. Semi-automatic machines require you to grind and tamp the beans on your own however the pump controls the flow of water and pressure. This is a great compromise between the human touch and mechanized quality.
The Filter
Typically, espresso machines employ a filter to separate out the coffee grounds as they pass through the hot water. The filter is also an important component of the temperature control system because it stops the machine from overheating.
A filter also improves flavor because it allows for a longer flowering phase. This lets the beans release their nuances, and improves extraction.
It is important to remember that even the most efficient filter can result in a bad cup of coffee. The quality of the beans, as well as the extraction, are still crucial.
This is where the magic happens. It's what makes espresso taste good. The grouphead (also known as the brewhead) is where you place the portafilter, which is the thingy that you put the grounds of coffee into when making espresso.
In the steam-driven espresso machine hot water is heated in an airtight container to create steam, which then pushes the hot water through the grounds under high pressure. They are less expensive and easier to maintain than pumps-driven models. However, they are limited in their ability to create the perfect brewing conditions since they are only operating at 1-1.5 bars of pressure, while the perfect shot requires 9-10 bar.
 In recent years, espresso machines driven by compressed air-pump have become increasingly popular. They use an air compressor to force hot water through the ground and Coffeee are much more mobile than electric steam-driven espresso machines.
In recent years, espresso machines driven by compressed air-pump have become increasingly popular. They use an air compressor to force hot water through the ground and Coffeee are much more mobile than electric steam-driven espresso machines.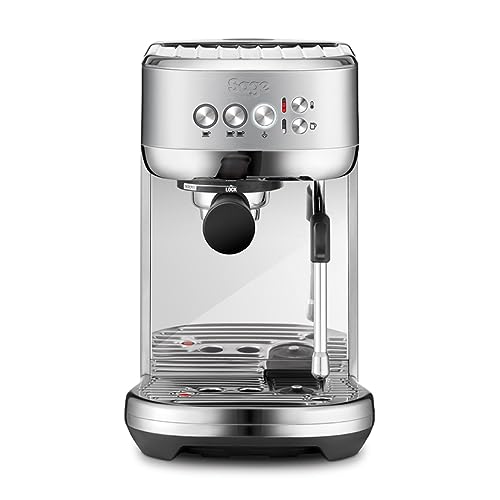
Machine espresso utilizes precise pressure and amazing filter technology to make the coffee we love. What exactly does it work?
Espresso is created by forcing hot water under pressure through finely ground coffee. The process is similar to making drip coffee, but the difference is in the pressure.
The Group Head
As the name suggests, the group head is where you insert your portafilter when brewing espresso. It distributes water into the portafilter and regulates the pressure of extraction. There are many different types of group heads, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some are designed to provide temperature stability while others are built to handle pre-infusion. Others are made to control the lever. Some have a combination, such as the E61. This is a preferred choice for baristas because it offers multiple benefits in one package.
As you can see in the image above the group head comes with several notches where you place your portafilter before twisting it manually to secure it. A gasket made of rubber is positioned within the notches to make a seal when you insert your portafilter. The notches allow for the precise placement of the portafilter. This is crucial for an even extraction.
The group head is not just able to allow you to put in your portafilter easily, but it also maintains the temperature at a constant level. It does this by cycling hot water through the brew container and around the portafilter, making sure that it's always at the right temperature to extract. This is vital, because even a small difference in temperature can make the difference between a excellent and great espresso.
The Pump
Unlike manual piston machines, which rely on a lever that pressurize water, rotating espresso machines rely upon motorized pumps that provide the nine atmospheric bars of pressure required to extract espresso. This pressure is built up by pumping water through a heat-exchanger and then through the ground coffee.
Pumps are generally cheaper and last longer than piston-driven machines. However, both kinds of machines may degrade due to excessive use and inadequate cleaning. They also add mechanical complexity which can result in the cost of even the simplest models.
Certain espresso machines utilize steam pressure instead of a pump to brew espresso. This can result in over-extraction because the boiler that makes steam also warms the water to boil. The machines also need to constantly rebuild their pressure between cups. This requires energy and time.
Many espresso machines employ the rotary or vibration pump, which has a vibration model using a vibrating disc to generate the pressure and the rotary model pushing hot water through the grounds under high speed. Both types of machine are capable of producing excellent espresso, but the rotary pumps are quieter, and more durable than vibration pumps.
The Boiler
The boiler is the element that heats water to the optimal temperature to extract. The steam produced reaches the portafilter, which contains the espresso coffee grounds. It is then poured into the cup. In this process, the steam creates pressure to push through the grounds of the coffee. This creates a foam on top of the espresso. This is the hallmark of a great espresso.
There are three kinds of espresso machines, each having a different type of pump and the temperature of the brew. There are different ways to control the amount of brew, as well as the size of cup that can be produced by the machine.
The first espresso machines were steam-types. The earliest espresso machines were steam-type machines. This led to the coffee tasting bitter and Coffeee burnt. This is why Milanese manufacturers Luigi Bezzerra and Desiderio Pavoni invented the modern Gaggia RI8425/11 Espresso Machine: Quality Freestanding Silver machine.
The most well-known espresso maker is a semi-automatic device that has an electric pump. These are the images people have when they think of an espresso maker. Semi-automatic machines require you to grind and tamp the beans on your own however the pump controls the flow of water and pressure. This is a great compromise between the human touch and mechanized quality.
The Filter
Typically, espresso machines employ a filter to separate out the coffee grounds as they pass through the hot water. The filter is also an important component of the temperature control system because it stops the machine from overheating.
A filter also improves flavor because it allows for a longer flowering phase. This lets the beans release their nuances, and improves extraction.
It is important to remember that even the most efficient filter can result in a bad cup of coffee. The quality of the beans, as well as the extraction, are still crucial.
This is where the magic happens. It's what makes espresso taste good. The grouphead (also known as the brewhead) is where you place the portafilter, which is the thingy that you put the grounds of coffee into when making espresso.
In the steam-driven espresso machine hot water is heated in an airtight container to create steam, which then pushes the hot water through the grounds under high pressure. They are less expensive and easier to maintain than pumps-driven models. However, they are limited in their ability to create the perfect brewing conditions since they are only operating at 1-1.5 bars of pressure, while the perfect shot requires 9-10 bar.
 In recent years, espresso machines driven by compressed air-pump have become increasingly popular. They use an air compressor to force hot water through the ground and Coffeee are much more mobile than electric steam-driven espresso machines.
In recent years, espresso machines driven by compressed air-pump have become increasingly popular. They use an air compressor to force hot water through the ground and Coffeee are much more mobile than electric steam-driven espresso machines.